Video KYC (Know Your Customer) is poised to revolutionize identity verification in the financial services sector. Yet at the same time, deepfakes are on the rise. There was a 10x jump globally in detected deepfakes in 2023—with the financial services industry being the second most targeted sector.
The shadow of KYC deep fakes looms large over video KYC. Deepfakes undermine the integrity of video KYC processes by creating realistic-looking videos that can deceive financial institutions into believing they are interacting with legitimate customers. This opens the door to fraudulent activities, identity theft, and other financial crimes.
This is why it’s critical to understand KYC deep fakes and develop comprehensive countermeasures against them so that the financial services industry can make the most of video KYC—confident that it is a secure means of identity verification.
What is Video KYC?
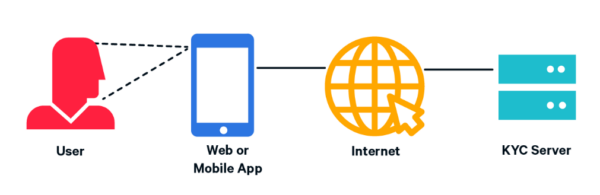
An alternative to traditional in-person KYC, video KYC is a remote, digital process of verifying a customer’s identity through a live video interaction. With video KYC, banks, financial institutions, and other regulated entities can onboard new customers and complete KYC requirements without physical contact.